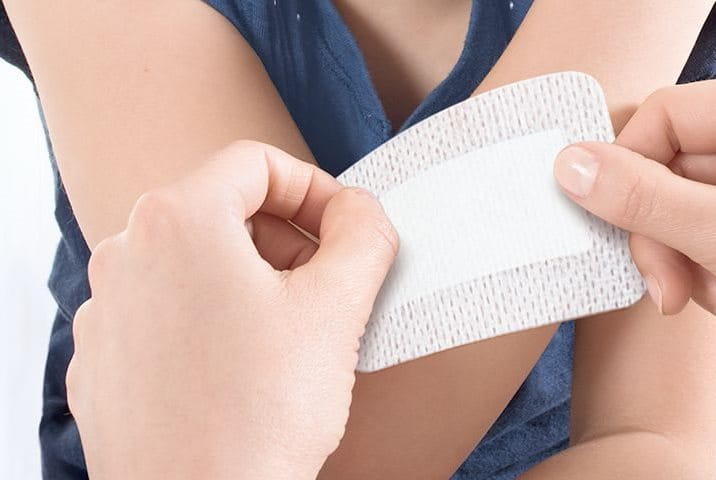
Surgical wound conditions
Surgical wounds are incisions performed in a medical setting. They are generally closed with sutures and professionally dressed, but still require the correct aftercare once you leave the hospital.
Treat surgical wounds in 3 steps
In order to take care of your post-op surgical wound, follow the instructions of your doctor. In alignment with the doctor, use these three quick and easy steps to ensure safe and fast healing.
How long is the healing process?
Following the procedure, your surgeon often uses sutures or surgical glue in order to close the wound, which approximates the wound edges to allow the wound to heal faster. Depending on the wound and body area, sutures will be removed after 5 to 14 days. Proper care according to the doctor’s recommendation is important until the post-operative wound has healed completely. The healing time depends on its size and location. Underlying illnesses like diabetes as well as age can also influence the healing process, with older patients’ wounds sometimes requiring more time.
Surgical wound infection
As with any type of wound, it is important to keep an eye on healing progress and watch for signs of wound infection after surgery. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience excessive redness or swelling around the wound or sutures, unpleasant smell or discharge, or if you feel warmth. While you may experience some post-operative pain following a procedure, these symptoms or additional pain could indicate an infection.
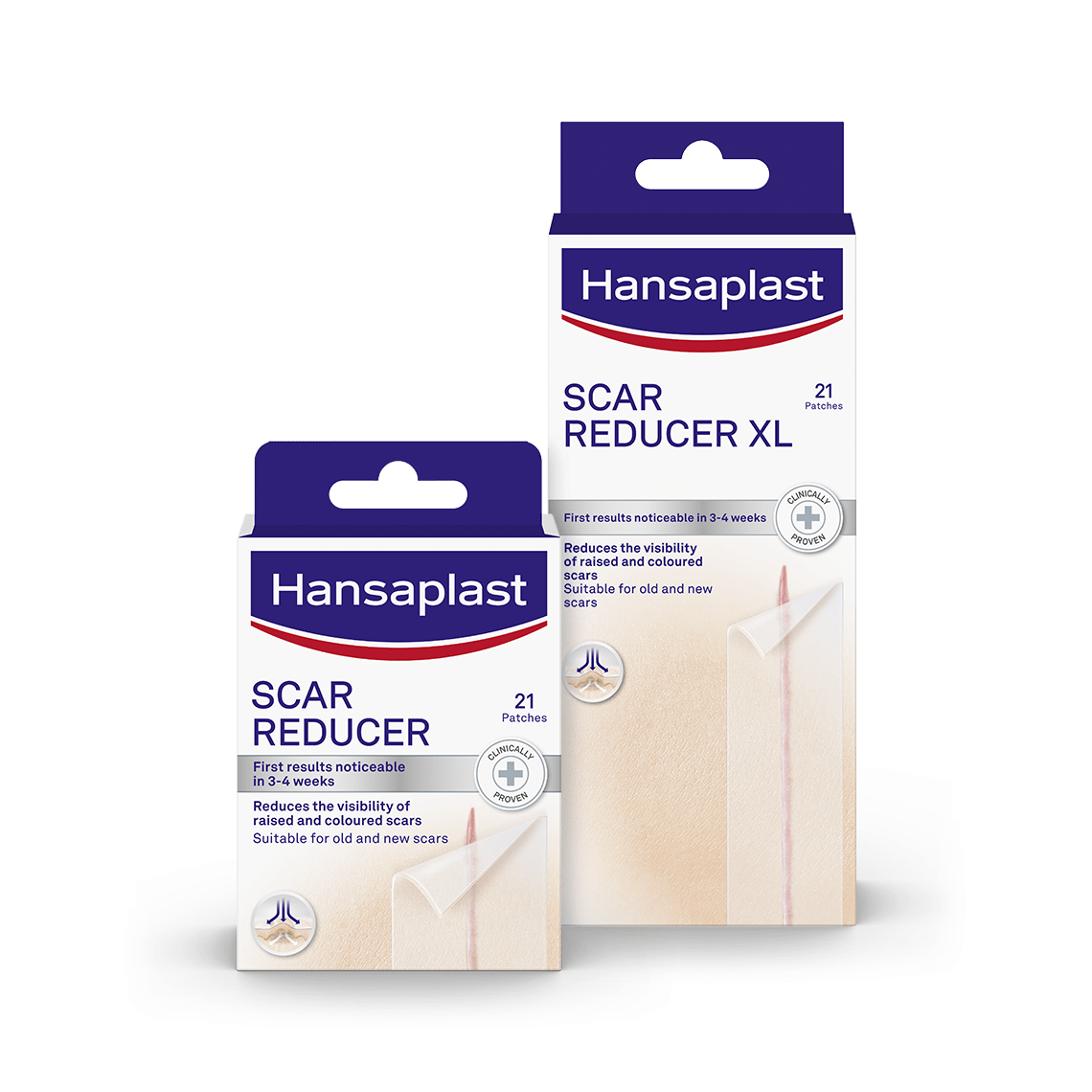
Surgical wounds and scars
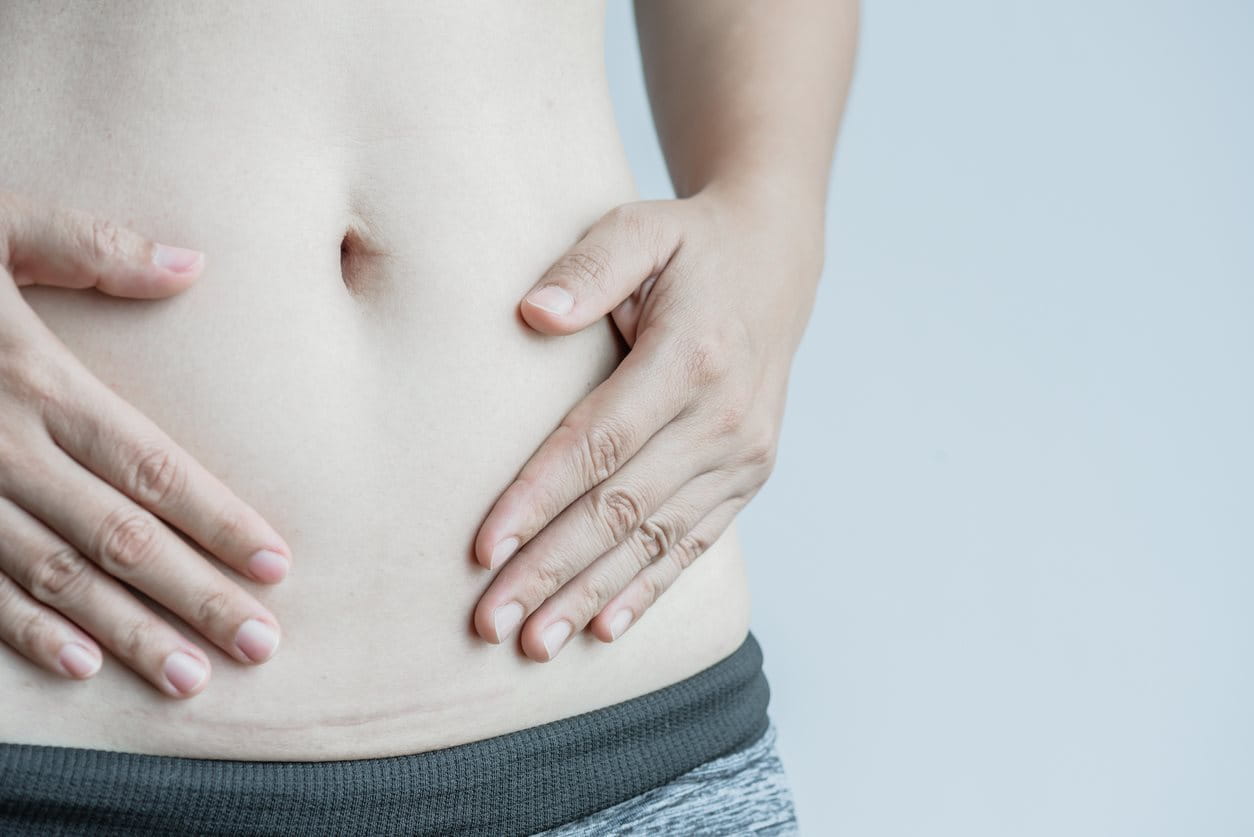
Scarring can occur at the end of the healing process of injuries that affect the epidermis and underlying dermis because the organism is not able to replace the destroyed, highly specialised tissue in the same way. Instead, the tissue is repaired by large amounts of newly produced collagen. To help reduce scarring, follow these simple tips:
Your doctor will advise you on how to treat your surgical wound depending on your situation.